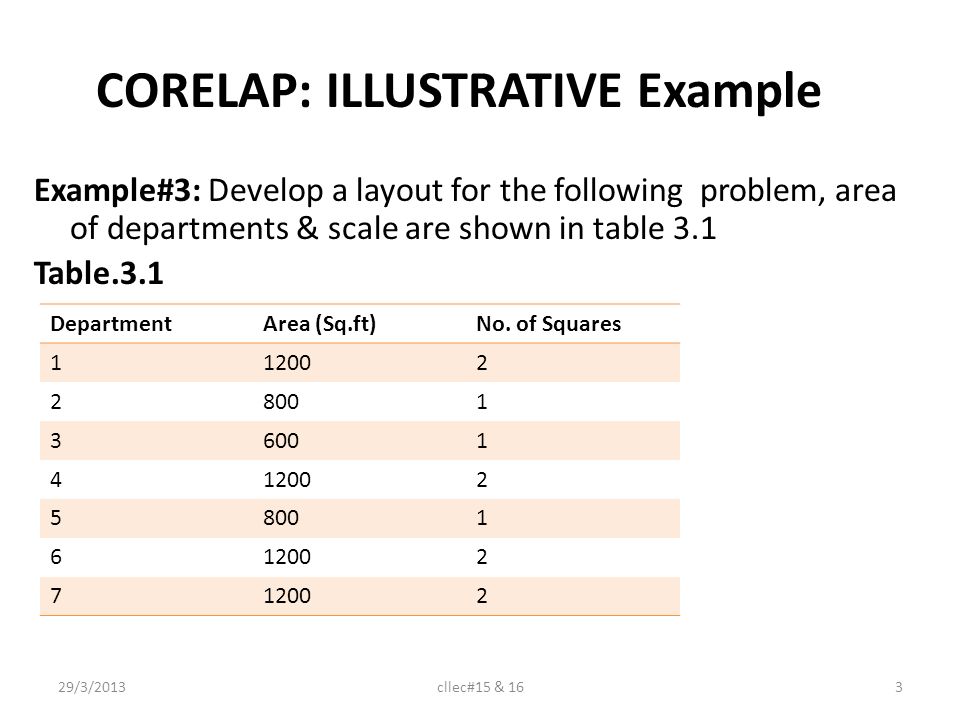
Corelap Layout Software

4, Number of Departments, 9, REL, Weight, REL, Cutoff. 5, Partial Adjacency, 0.5, A, 125, A, 575. 6, Layout Score, 0, E, 25, E, 375. 7, I, 5, I, 175. 8, O, 1, O, 35.
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT ASSIGNMENT Topic: COMPUTERIZED LAYOUT ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES Submitted By: SAMYADIP CHAKRABORTY MOHD. ABDUL NAYEEM PhD Batch -2010 COMPUTERIZED LAYOUT ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES In the field of computerized layout analysis, a number of computerized layout programs have been developed since the 1960s and 70s. But the most time tested computerized layout techniques and software program packages that are frequently used are- CRAFT, CORELAP, ALDEP, etc. Originally developed in late 60’s and early 70s, many of these packages are still around with latest additions to their features. Layout problems often involve a given number of facilities which must be located in the plane. Each of these facilities has a given area, and the cost of interactions between every facility pair is known.
Problem optimality is achieved when facilities do not overlap and the total cost, which is the sum of weighted distances between all pairs of facilities, is minimized. CRAFT (Computerized Relative Allocation of Facilities Technique) CRAFT (Computerized Relative Allocation of Facilities technique) is the most widely applied.
CRAFT algorithm was originally developed by Armour and Buffa in the 1970s. It is more widely used than ALDEP and CORELAP. It starts with an initial layout and improves the layout by interchanging the departments pair-wise so that the transportation cost is minimized. CRAFT method uses the same basic idea used for a factory layout with certain significant operational differences. It requires a load and a distance matrix as initial inputs and also feeds in data regarding the cost involved per unit distance moved. With these inputs and an initial layout in the program, CRAFT attempts to improve the relative placement of the departments as measured by total material handling cost for the layout. CRAFT is a method of “successive” improvements.
CRAFT uses a pair wise exchange to develop an improved layout. It makes improvements by exchanging pairs of departments iteratively until no further cost reductions are possible. The program calculates the effect on the total cost of exchanging departments; if this leads to a reduction, the change is made and it leads to iteration. My little pony games free. The CRAFT requirements are: Initial layout Flow data Cost per unit distance Total number of departments Area of departments The CRAFT model represents a breakthrough in the ability to systematically evaluate layout problems having complex flow. The superiority of results obtained by earlier techniques was in no small way dependent upon the art of the layout analyst. The CRAFT model can generate and evaluate layouts having as many as 40 departments in less than one minute of computer time. In addition, any department or departments may be fixed in particular locations.